Learning Human-Human Interactions in Images from Weak Textual Supervision
ICCV 2023
How are these people interacting?
(Hover to see the output of a model trained on our
pseudo-labels.)
Human-human interactions (HHI) in images are diverse and cannot be easily described by a fixed set of categories. They often rely on contextual cues (e.g. the clothes and cake in the first image) and may involve participants at a distance (as in the last image).
In this work, we propose to model HHI understanding in images as free text generation to capture the vast variety of ways in which people interact, learning them by training a model to produce HHI pseudo-labels from Internet image captions. We provide the Waldo and Wenda benchmark for this task along with an evaluation framework, and show that training on our pseudo-labels improves HHI understanding beyond SOTA captioning and situation recognition models.
Abstract
Interactions between humans are diverse and context-dependent, but previous works have treated them as categorical, disregarding the heavy tail of possible interactions. We propose a new paradigm of learning human-human interactions as free text from a single still image, allowing for flexibility in modeling the unlimited space of situations and relationships between people. To overcome the absence of data labelled specifically for this task, we use knowledge distillation applied to synthetic caption data produced by a large language model without explicit supervision. We show that the pseudo-labels produced by this procedure can be used to train a captioning model to effectively understand human-human interactions in images, as measured by a variety of metrics that measure textual and semantic faithfulness and factual groundedness of our predictions. We further show that our approach outperforms SOTA image captioning and situation recognition models on this task. We will release our code and pseudo-labels along with Waldo and Wenda, a manually-curated test set for still image human-human interaction understanding.
Our Method
Internet image captions often contain weak cues to HHI, which are not confined to a specific syntactic category such as verbs and which may be surrounded by many irrelevant details. To overcome these challenges, we infer interactions from the original captions by applying knowledge distillation to synthetic data generated by a large language model, without explicit supervision. We prompt a teacher large language model (LMT) to produce synthetic captions corresponding to given interactions, including seed in-context examples and filtering with a natural language inference (NLI) model and text heuristics.
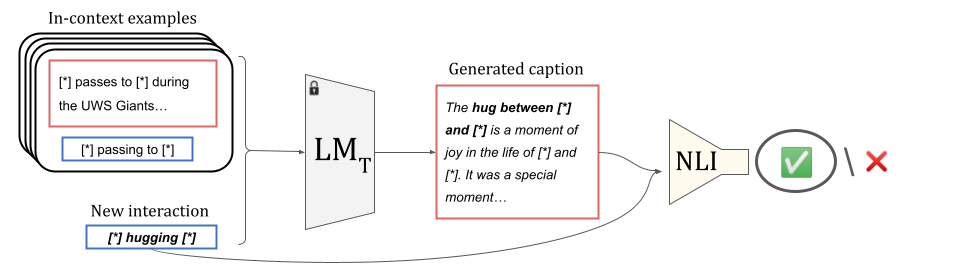
We train a smaller student language model (LMS) on these synthetic caption-interaction pairs, teaching it to summarize HHI from captions. We then apply this model to the captions in Who's Waldo to produce HHI pseudo-labels for the images in the dataset.
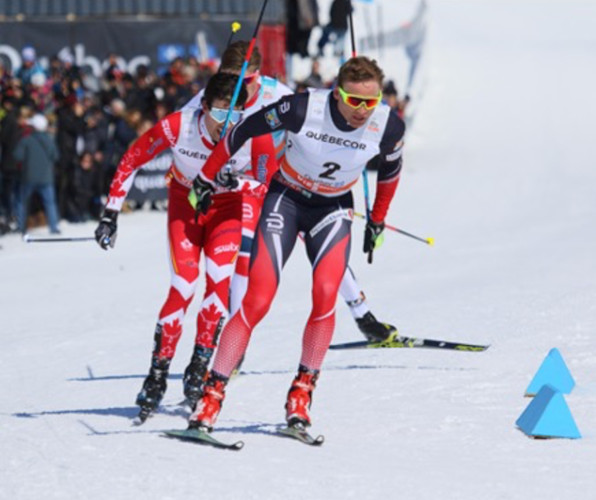

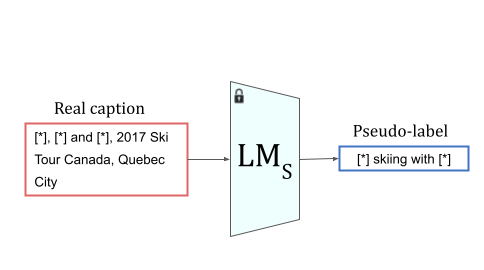
Finally, we use these pseudo-labels to fine-tune image captioning models for HHI understanding.
Interactive Visualization
See our interactive visualization for results of all models on the 1K-item Waldo and Wenda HHI benchmark and the >8K-item imSitu-HHI subset of the imSitu situation recognition benchmark.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ron Mokady for providing helpful feedback. This work was supported by a research gift from Meta and the Alon fellowship.
Citation
@InProceedings{alper2023learning,
author = {Morris Alper and Hadar Averbuch-Elor},
title = {Learning Human-Human Interactions in Images from Weak Textual Supervision},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV)},
year = {2023}
}



